As you can guess from our name, we at Electric Power Systems specialize in everything to do with electrical infrastructure. We have the right knowledge and experience to help you keep every part of your system in good working order, and that includes components like the inductors. Two of the most common types of inductors are air and iron core models, and in this article, we’ll go over some key differences between them to help you decide which is best for your needs.
What are Inductors?
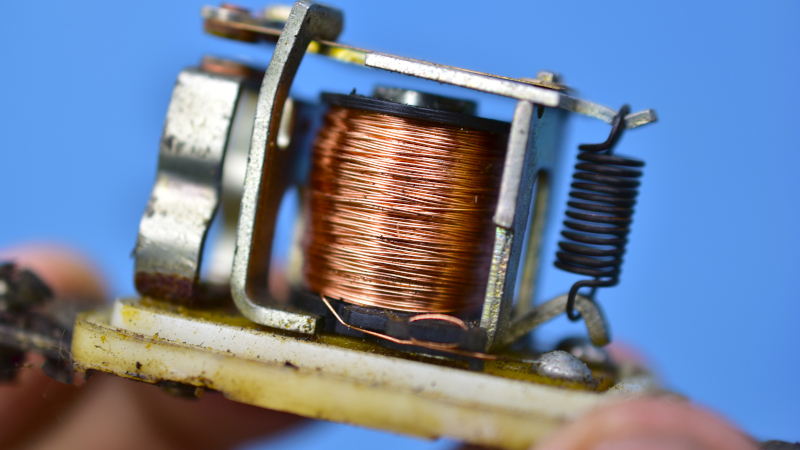
Before we cover the differences between these types of inductors, let’s slow down and define what inductors are in general. Inductors are electrical components that store energy in magnetic fields when electrical current runs through them. They are passive, two-terminal components that typically consist of an insulated wire wound into a coil.
- Air Core Inductors- The term “air core inductors” is used to describe all inductors that do not use ferromagnetic material in their cores. Instead, air core conductors may use plastic, ceramic, or other nonmagnetic materials, or have only air inside the windings. While these inductors provide lower inductance than iron core inductors, they are generally more effective at high frequencies and don’t suffer as much core loss.
- Iron Core Inductors- As their name suggests, iron core inductors use magnetic cores of iron or ferrite. They generate a higher level of inductance than air core inductors, so there is typically some energy lost in the process.
Our team can help you decide which variety is right for your needs, and we encourage you to give us a call.
